In this tutorial, we will cover difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM and their component.
Table of Contents
Difference between JDK, JRE and JVM
JDK(Java Development Kit):- The Java development kit is a software development environment to develop the java applications. It contains Java Run Time Environment (JRE) and development tools like a compiler (Javac), an interpreter, a document generator (Javadoc) and other tools.
Download JDK
To download the JDK, Please visit the official site of Oracle
Click here to Download JDK
Set JDK Path/JAVA_HOME path in Environment Variable – Click here to see the steps of set the path
JRE (Java Runtime Environment):- It is the implementation of the JVM. It provides a platform to run the java programs. It consists of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), core classes and supporting files.
JRE = JVM + Library Classes(Java API)
JVM (Java Virtual Machine):- JVM is the main part of the Java language which is responsible for to read the bytecode and execute it.
JVM performs the following main tasks:
· Loads code
· Verifies code
· Executes code
· Provides runtime environment

Let’s understand the Architecture of JVM
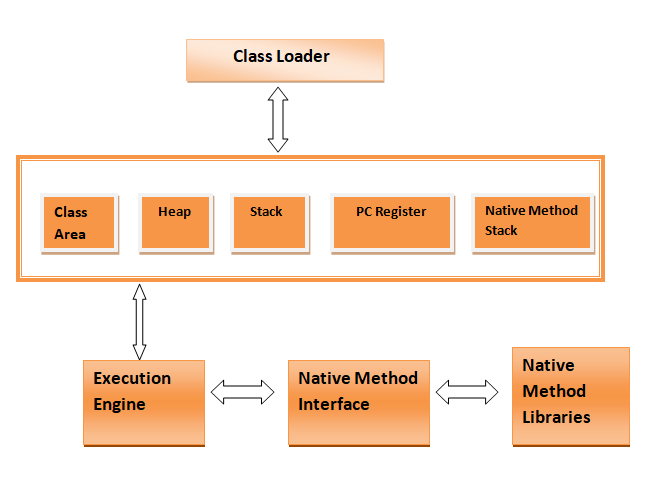
ClassLoader: It is a subsystem for loading the class. When we run the java program it first loaded by the classloader.
Class Area: JVM class area stores the class structure like runtime constant pool, field, method data.
Heap: It is a runtime memory area for instance variables, arrays object etc.
Stack: It stores local variables, and it’s partial results. A new frame is created when a method is invoked and it is deleted when this method is complete.
PC register: Program counter register stores address of the Java virtual machine instruction.
Native Method Stack: It contains all native method used in the application. It is a different language instead of java.
Execution Engine: It contains:
Virtual Processor
Interpreter:– Read bytecode and execute it.
Just-In-Time Compiler:- It is used to improve the performance of the compiler. It compiles the bytecode hence it reduces the time needed of compilation.
Native Method Interface: The native method interface is a programming framework which provides an interface to communicate with other application written in another language.
Java uses the JNI framework to send output to the console.